Case Study: How University of Antwerp differentiated COVID-19 disease severity with T Cell signatures
Discover how MiXCR + QIAGEN streamline TCR sequencing and accelerate breakthroughs in immune research
Background: Challenges in Population-Level T Cell Profiling
Traditional seroepidemiology, the study of antibodies in populations, has been central to understanding infectious disease dynamics. However, antibody levels often wane quickly, vary by disease severity, and provide a limited view of long-term immunity. During the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers sought to go beyond serology to measure T cell–mediated immunity, which is often more durable and nuanced.
Objective: What is Celluloepidemiology and Why It Matters
To address this gap, the team at the University of Antwerp introduced celluloepidemiology, a paradigm leveraging population-level T cell profiling and TCR sequencing to more accurately quantify infection dynamics, identify hidden infections, and stratify disease severity in large populations.
Challenge:
Celluloepidemiology offered transformative potential, but faced key barriers:
Reproducibility in Library Prep: To study hundreds of samples, researchers needed a standardized, high-quality workflow for TCR sequencing libraries; variability could have undermined results.
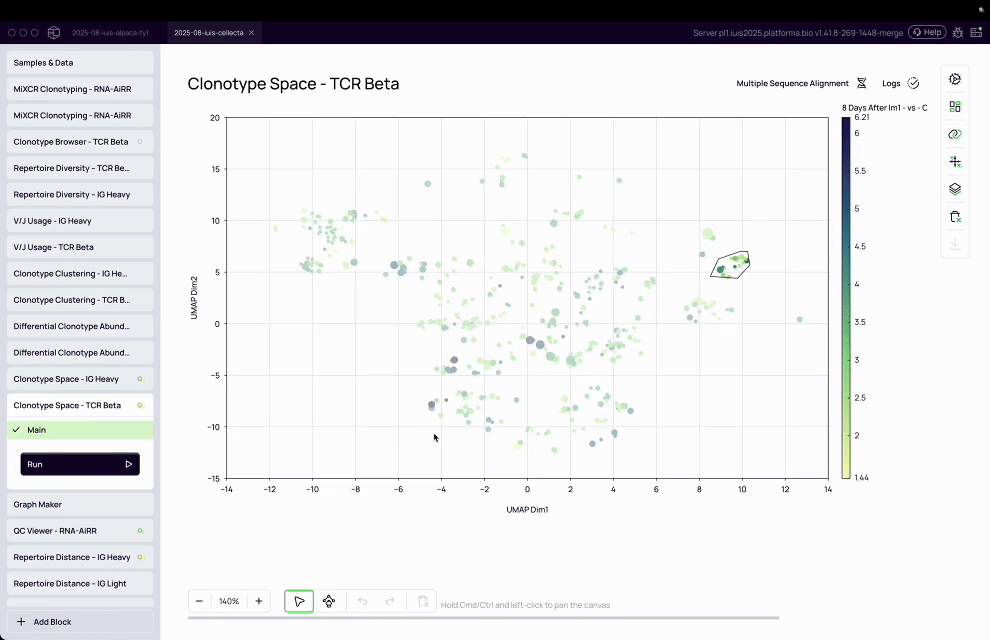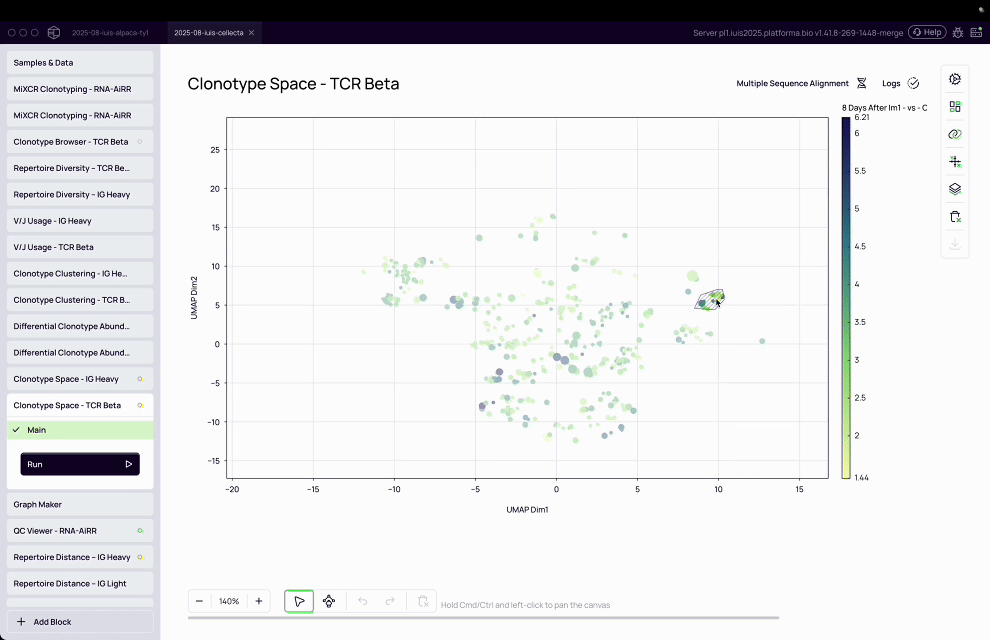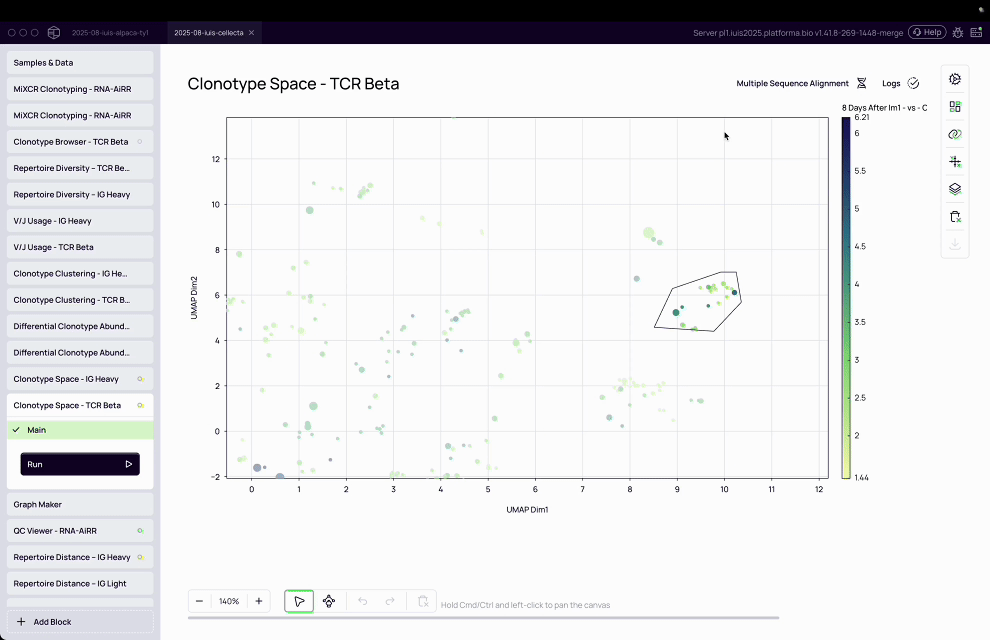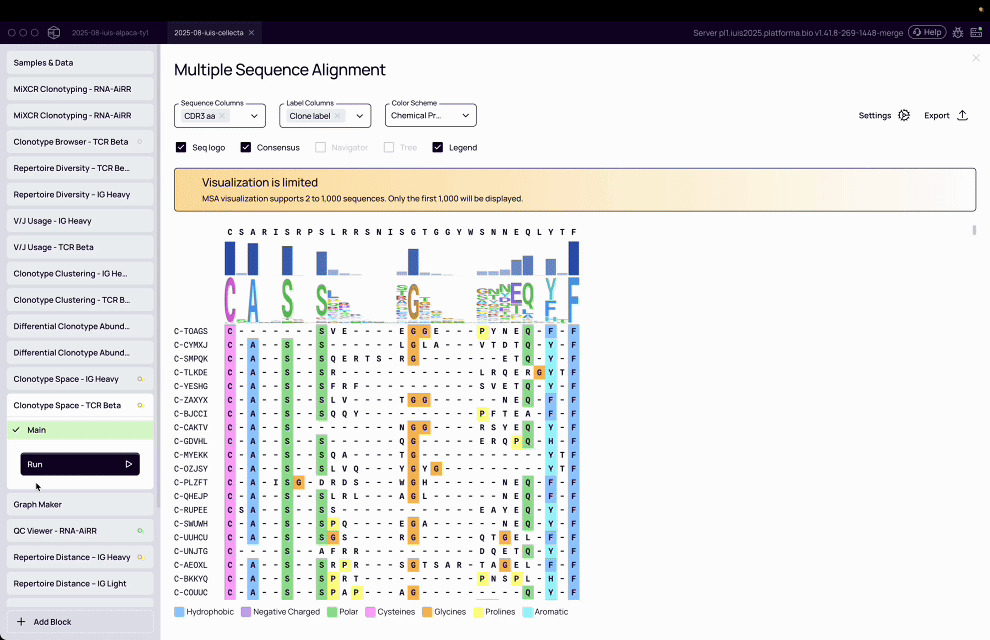
Complexity of T-cell analysis: T-cell assays are inherently multi-parameter, with T-cells expressing a diversity of proteins on their surface, requiring advanced computational tools to cluster, classify, and interpret patterns.
Cross-reactivity risks: T cells often target epitopes shared across coronaviruses, demanding precise sequence-level analysis to avoid false signals.
Without strong wet-lab and computational solutions, scaling celluloepidemiology to population studies would not be practical.
Solution: QIAGEN + MiXCR-Powered TCR Profiling
The research team integrated QIAGEN’s standardized library prep with MiXCR’s computational engine, enabling scalable and validated TCR repertoire analysis.
QIAGEN QIAseq Immune Repertoire RNA Library Kit delivered scalable, reproducible, and high-quality TCR libraries, ensuring comprehensive capture of immune diversity across hundreds of samples.
MiXCR transformed raw sequencing data into actionable immune insights by assembling clonotypes, clustering TCRs, and annotating antigen specificity at population scale.
Beyond QIAGEN and MiXCR, the study also leveraged flow cytometry and other technologies to provide complementary phenotypic and antibody-based insights alongside TCR repertoire analysis.
“MiXCR + Qiagen offers a solution to sequence all four TCR chains in a single kit. This is a large benefit for us, as it is often unknown in advance if we are searching for an αβ or γδ lineage T-cell. “
- Pieter Meysman, Associate Professor at the University of Antwerp
Results and Impact:
The celluloepidemiology approach demonstrated significant capabilities beyond conventional serology:
Uncovered hidden infections: The study identified asymptomatic cases missed by antibody testing.
Stratified disease severity: T cell markers and TCR repertoires correlated with mild, moderate, and severe COVID-19.
Differentiated healthcare workers: Groups indistinguishable by serology showed distinct TCR repertoire signatures.
Characterized long COVID: Patients with persistent symptoms exhibited unique T cell activation and exhaustion profiles.
Validated immunity: SARS-CoV-2–specific TCR clusters were enriched in recovered patients.
The Qiagen chemistry cut prep time by 25%, accelerating sample to insight and enabling faster scientific discoveries.
“MiXCR works out of the box with the Qiagen chemistry to handle VDJ processing, so you can go from raw FASTQ files to clonotypes in a single command. We know that we get the maximum quality output from our sequencing experiments.”
The study concludes that the celluloepidemiology paradigm is complementary to seroepidemiology, providing high-dimensionality, sensitivity, and deep insights into the heterogeneity of human immune responses. This framework unlocks powerful new possibilities, with applications that extend far beyond COVID-19 to transform how we study infectious diseases, monitor vaccine effectiveness, and advance public health surveillance worldwide.
Read the full article in Science: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adt2926
Learn more about QIAseq TCR-seq kits and get access to MiXCR, through Platforma’s intuitive user interface.